Commerce has changed fast. Customers move fluidly between physical and digital spaces, expect instant access to information, and increasingly prefer contactless, mobile first interactions. Understanding how QR codes work for commerce is no longer a technical curiosity. It is a practical requirement for modern businesses.
This article explains how QR codes work for commerce inside QRCodeKIT, focusing on real workflows rather than theory. The goal is to help you understand how QR codes support payments, marketing, and customer journeys without turning this into a sales pitch or a generic QR code guide.
How QR codes work for commerce in real world scenarios
At their core, QR codes connect a physical touchpoint to a digital action. In commerce, that action usually involves accessing information, completing a payment, or continuing a journey that started offline.
When a customer scans a QR code using a smartphone camera, the code is decoded instantly and opened through the device’s web browser or payment app. This removes friction compared to typing URLs or manually entering payment details, which many shoppers actively prioritize during checkout.
In commerce contexts, QR codes work because they reduce steps. A single scan can take a customer from a checkout counter, product page, or marketing material directly to a payment page, online store, or landing page designed for that moment.
Static and dynamic QR codes in commerce use cases
One of the most important distinctions in commerce is between static QR codes and dynamic QR codes.
A static QR code contains fixed information. Once printed, it always points to the same destination. This can work for simple, unchanging uses, but it limits flexibility. If the payment information, checkout page, or campaign changes, the QR code must be replaced.
A dynamic QR code works differently. The QR code itself stays the same, but the destination can be updated at any time. Inside QRCodeKIT, this means a single QR code can support evolving customer journeys without reprinting packaging or marketing materials.
For commerce teams, this flexibility matters. Dynamic QR codes allow businesses to adapt payment methods, update product pages, or refine marketing campaigns while keeping the same physical code in use.
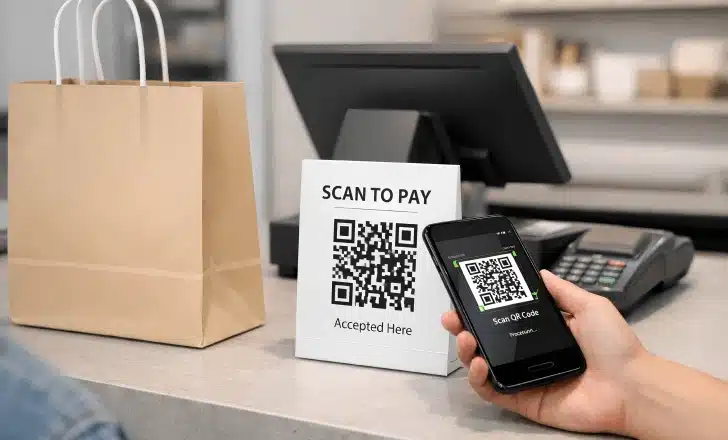
How QR code payments work from scan to confirmation
QR code payments follow a straightforward flow. A customer scans a payment QR code at a checkout counter, on a receipt, or on a screen. The scan opens a payment page or payment service provider interface on the customer’s mobile device.
From there, the customer selects a preferred payment method such as a digital wallet or credit card. Mobile wallets like Apple Pay or Google Pay streamline this step by handling payment information securely without manual data entry. Once the transaction amount is confirmed, the payment is processed through the merchant account.
This approach reduces wait times and removes the need for traditional POS card readers or paper receipts. It also supports contactless payments, which many consumers now expect as part of a modern customer experience.

QR codes as both a payment method and a marketing tool
In commerce, QR codes rarely exist in isolation. A payment QR code is often part of a broader QR code marketing strategy.
For example, the same QR code that opens a payment page can also guide customers to exclusive discounts, loyalty programs, or customer feedback forms after the transaction. This turns a single scan into a connected journey that supports conversion rates and customer retention.
Because QR codes link physical and digital touchpoints, they are especially effective for directing customers from offline materials to online shopping experiences or ecommerce platforms.
Using QR codes to connect physical stores and ecommerce
QR codes are particularly effective when commerce spans physical and online locations. In store QR codes can link directly to product pages, payment information, or an ecommerce store checkout page.
This is useful when inventory is limited in store, when customers want more product context before making purchases, or when businesses want to measure engagement metrics tied to specific locations or campaigns.
By placing QR codes on shelves, packaging, or displays, businesses create a seamless path for customers to continue their journey online.
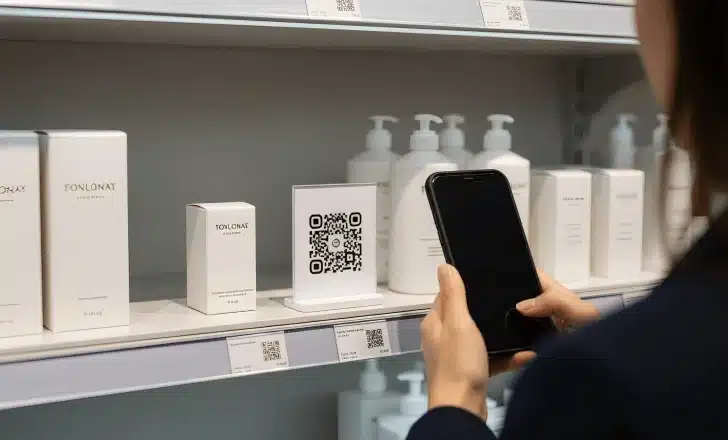

What happens technically when a customer scans a QR code
From the user’s perspective, scanning feels instant. Behind the scenes, several steps happen almost immediately.
The device’s camera recognizes the positioning markers and decodes the QR code. The encoded URL or payment information is then opened using the smartphone’s default browser or payment app. With dynamic QR codes, the scan is routed through a secure redirect before sending the customer to the final destination.
This process allows businesses to track scan data such as device types, time, and location while keeping the experience smooth for customers. Built in error correction ensures QR codes remain scannable even if part of the code is damaged.
Security and trust in QR code payments
Security is a common concern when discussing QR code payments. In practice, QR codes can enhance security by minimizing manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors.
Dynamic QR codes can use transaction specific data and encrypted redirects, helping protect payment information during checkout. Customers do not need to type sensitive details into unfamiliar interfaces, since payments are handled by established payment service providers.
This balance of speed, accuracy, and trust is a key reason QR code payments continue to grow in popularity among consumers and businesses.
Measuring engagement and performance with dynamic QR codes
Beyond payments, QR codes provide valuable insights into customer behavior. Dynamic QR codes allow businesses to track engagement metrics such as scan frequency, location, and timing.
These insights help teams understand which marketing materials perform best, how customers move between physical and digital touchpoints, and where journeys can be improved. Over time, this data supports more informed marketing strategies and better customer experiences.
When QR codes make the most sense in commerce
QR codes are especially effective in environments where speed, convenience, and flexibility matter. Coffee shops, events, pop up retail, and omnichannel businesses benefit from the low cost and instant access QR codes provide.
They are also useful for ecommerce brands that rely on offline marketing materials or social media platforms to drive traffic to online shopping experiences.
The key is using QR codes intentionally and always connecting each scan to a clear next step.

Learning more about QR codes inside QRCodeKIT
QR codes are most effective in commerce when they are designed around real customer behavior rather than novelty. Inside QRCodeKIT, QR codes are treated as adaptable connectors that can evolve as customer journeys change.
If you want to explore how different QR code types support payments, marketing campaigns, and customer journeys, learning more about how QRCodeKIT structures dynamic QR codes can help you design clearer, more flexible experiences without unnecessary complexity.