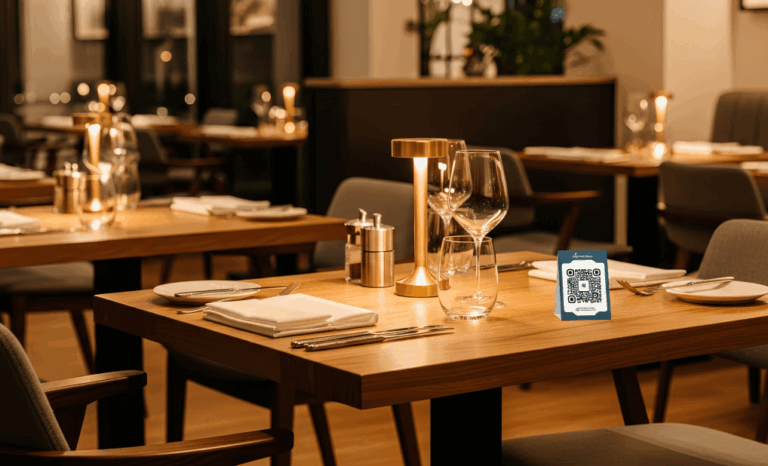
What exactly is a QR code and why is it everywhere?
You’ve seen them on milk cartons, menus, packages, posters—even tattoos. QR codes are those black-and-white pixelated squares popping up just about everywhere. But they’re more than a tech trend or marketing gimmick. They’re powerful connectors, designed to deliver instant information with a single scan.
Short for Quick Response, a QR code is a compact square that stores data in a two-dimensional matrix. Unlike old-school barcodes that only work in one direction, QR codes can be read both horizontally and vertically. That’s how QR codes work—they pack more data into less space, making them capable of storing everything from URLs and contact details to videos and payment info.
Scanning is effortless. Just open your phone’s camera (or a dedicated app), point it at the code, and boom—you’re taken straight to whatever it holds. No typing. No guesswork.
They’re tough, too. Built with error correction, QR codes can still work even if they’re smudged, scratched, or partially damaged. Think of them like the cockroach of scannable tech—resilient and reliable.
And then there’s the flexibility. Static QR codes stay fixed—they always link to the same thing. But dynamic QR codes? They let you change what they link to without touching the printed code. That makes them perfect for campaigns, product packaging, and any situation where content evolves over time.
Bottom line: QR codes aren’t just little boxes of black and white—they’re the backbone of how we interact with the physical world in a digital age. Once you understand how QR codes work, you’ll never look at them the same way again.

Historical overview
The story of the QR code begins in 1994, in Japan’s automotive industry. A company called Denso Wave developed it to track car parts in the manufacturing process. It didn’t take long for its potential to outgrow the factory floor.
What made the QR code stand out was its ability to store significantly more data than traditional bar codes. That, plus its fast-scanning speed, opened the door to new possibilities.
As industries caught on, QR codes started appearing on packaging to deliver product details, special offers, or user manuals. They created a direct line between physical products and digital experiences—something no bar code could do.
The real turning point came with the rise of smartphones. Suddenly, anyone with a camera app or QR code scanner in their pocket could interact with the world in new ways. Posters turned into landing pages. Billboards led to event registrations. Business cards gained scannable contact info.
Then came the evolution: static QR codes for fixed info like WiFi passwords, and dynamic QR codes that could be updated behind the scenes—no need to reprint anything.
From contactless QR code menus at restaurants to boarding passes, museum tours, and payment screens, QR codes have become an everyday utility.
Today, they’re not just functional—they’re foundational. The QR code’s journey from factory tool to digital bridge shows just how adaptable and impactful this technology has become.
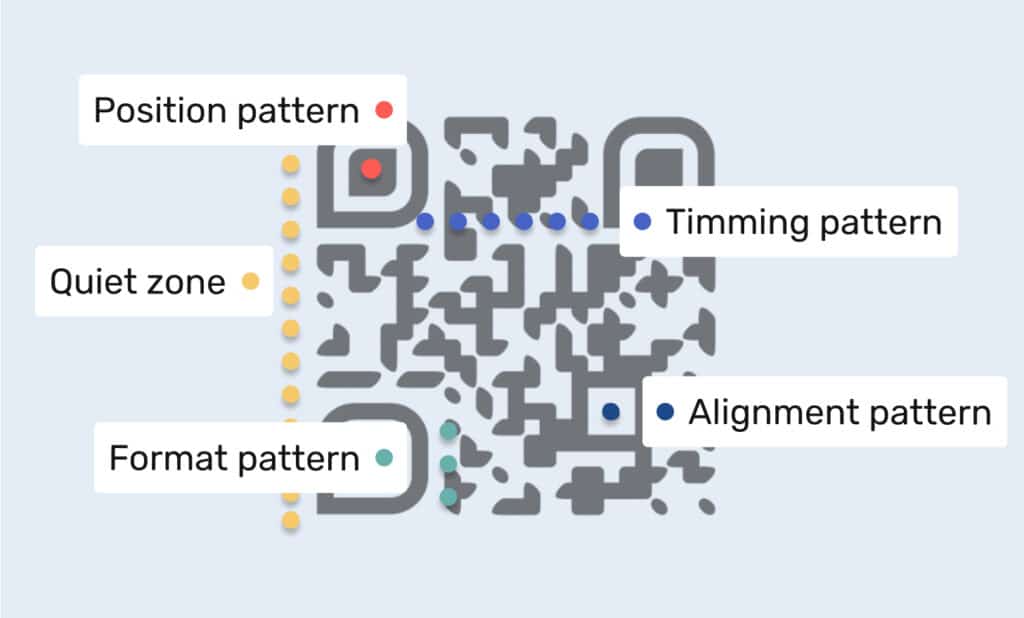
The basics: Black and white pixels
At first glance, a QR code looks like a random patchwork of black and white squares. But there’s method in the mosaic. Every square—every pixel—is part of a carefully crafted pattern that tells a digital story.
Here’s how it works: each black square is a binary “on,” and each white one is “off.” This simple system of 1s and 0s (aka binary code) forms the foundation of how QR codes store information—from web links to contact cards to login details.
The QR “eyes”
Those three bigger squares you see in the corners? They’re not just decorative—they’re called position markers. Located at the top left, top right, and bottom left corners, they help your QR code scanner or camera app figure out how the code is aligned. Whether it’s upside-down or slightly tilted, those markers make sure the scanner still reads it correctly.
The error correction method
And what if the code is smudged, scratched, or slightly torn? That’s where error correction comes in. QR codes use built-in redundancy—meaning even if part of the code is damaged, the data can still be recovered. It’s one of the reasons QR codes are so reliable and why they’ve become central to marketing and advertising campaigns, public signage, and more.
Some QR codes store basic text. Others, like dynamic QR codes, handle more complex data or allow updates after they’re created. The more intricate the pattern, the more information it holds—proving that behind every tiny pixel is a big potential.
How to scan a QR code
What makes QR codes so powerful is their ability to connect the physical and digital worlds in a single scan. Unlocking the information they hold is quick and easy—here’s how it works.
Acquire a QR reader
Most modern smartphones already come with a built-in QR code scanner right inside the camera app. Just point and scan. But if you’re after extra features—like a scan history, security checks, or advanced options—there are plenty of QR reader apps in the app store that offer more control and customization.
Position the QR code
Open your camera app or QR code reader and aim it at the QR code. Make sure the code is well-lit and clearly visible—those black and white patterns need to stand out. For the best scan, center the code and fill as much of the screen as possible without cutting off any edges.
Automatic scanning
Here’s where the magic happens. You don’t need to press anything. As soon as your camera locks onto the QR code image, it automatically reads the data. Your phone camera handles the scanning process in seconds, no matter what type of QR code it’s reading.
Safety first
But not all QR codes are created equal. Malicious QR codes can lead to phishing sites or trigger unwanted downloads. To stay safe, only scan QR codes from sources you trust. If a QR code scan brings up a sketchy-looking URL or unexpected prompt, it’s better to back out than click through.
Diverse applications
QR codes can take you just about anywhere—an Instagram page, a discount code, a QR code menu, or even a secure login link. Understanding the basics of scanning a QR code gives you access to an entire ecosystem of content, services, and experiences.
In a world that’s moving fast and going digital even faster, knowing how QR codes work—and how to use them safely—makes life smoother and more connected.

Static QR codes vs. dynamic QR codes
Not all QR codes are built the same. In fact, the QR code universe is divided into two main types: static QR codes and dynamic QR codes. Each has its own strengths, and knowing when to use which one can make a big difference in your strategy.
Static QR codes
Think of a static QR code like a printed flyer: once it’s made, the information is locked in. Whatever content you embed at the time of creation—whether it’s a URL, contact details, or a Wi-Fi password—that’s what the code will always point to. You can’t change it later.
That said, static QR codes are still incredibly useful. If you’re sharing information that never changes, they’re perfect. A static QR code is ideal for:
- Permanent website links
- Event flyers or brochures
- Business cards with contact details
- Printed materials where you won’t need to update the content
Because the data is stored directly in the QR code image itself, there’s no dependency on an external server. Just create the code, print it, and it’ll keep working—no maintenance required.
Dynamic QR codes
If static QR codes are set in stone, dynamic QR codes are more like whiteboards—you can update the content behind them at any time without changing the QR code itself.
Once a dynamic QR code is created, you can modify the destination (like a URL or file) without having to reprint or redistribute the code. The QR code image stays the same, but what it points to can change as often as you like.
Applications
This flexibility makes dynamic QR codes ideal for anything that needs to stay current. Running a marketing campaign and want to switch the landing page halfway through? No problem. Need to update a promotional link or track engagement with unique URLs? Done.
Restaurants often use dynamic QR codes for menus. As dishes change or seasonal items rotate in, the menu linked to the QR code can be updated instantly—no need to reprint every table card or placemat.
Other common uses include event schedules, product pages, real-time promotions, and any situation where content may shift over time.
Safety considerations
Because dynamic QR codes can be updated remotely, they do carry some security concerns. A malicious QR code could redirect unsuspecting users to a harmful site if the destination link is hijacked.
That’s why it’s essential to pick a QR code generator or platform that is well-known. You should go for one offering features like link monitoring and analytics. Using legit QR codes coming from reputable sources maintains scanning safety.
Data storage in QR codes
At first glance, QR codes might just look like a jumble of black and white squares. But don’t be fooled—these compact grids are surprisingly powerful when it comes to storing data.
Behind the pattern is a sophisticated system designed for both speed and capacity. A single QR bar code can hold up to 3,000 alphanumeric characters. That’s enough room for URLs, contact details, serial numbers, or even full messages—all packed into a tiny space that fits on a business card or product label.
As the data stored increases, so does the visual complexity of the code. More squares, denser patterns—but still scannable in an instant. It’s a key part of how QR codes work so efficiently.
And they’re tough, too. Thanks to error correction, even if part of the QR code gets smudged, scratched, or partially covered, your phone or QR code scanner can still read the information. That resilience is one of the main reasons QR codes work so well in the real world—where wear and tear is just part of the game.

Different types of QRs
QR codes aren’t one-size-fits-all. In fact, QR Code KIT offers a whole toolkit of specialized QR types, each designed for a specific task. Once you see how flexible they are, you’ll start to understand the full scope of how QR codes work in today’s digital landscape.
Here’s a breakdown of the most popular QR code types and where they shine:
- Website: Direct users to a specific website or webpage instantly.
- Landing page: Perfect for marketing and advertising campaigns, this QR redirects to a specially designed page that drives visitor action.
- Digital business card: Share contact details seamlessly. Scanning this QR offers instant access to phone numbers, emails, addresses, and more.
- PDF: Great for sharing documents, manuals, or brochures without physical copies. Just scan and access the PDF.
- Menu: Ideal for restaurants or cafes wanting to offer contactless menu viewing.
- App store: Provide users with instant access to download apps, bypassing the search process in app stores.
- Social media: Consolidate and share all social media profiles or pages in a single scan.
- WhatsApp: Initiate direct conversations on WhatsApp, facilitating customer service or personal chats.
QR Code KIT makes creating QR codes for all these purposes easy and accessible. Whether you’re sharing a vCard, launching a coupon campaign, or linking to a video, there’s a QR code built for that. It’s a reminder that QR codes store information far beyond just plain text—they connect people with experiences, instantly.

Popular uses of QR codes
QR codes have quietly become part of our everyday lives—and that’s no accident. Their ability to store information compactly and deliver it instantly makes them one of the most versatile tools in the digital world. From marketing to dining, let’s look at where QR codes are making the biggest impact.
Social media integration
QR codes have become a favorite shortcut to online visibility. Businesses, creators, and influencers use them to drive traffic to their social media profiles—you’ll find them on flyers, packaging, posters, even product tags. Just one scan and users are instantly connected, no searching required.
Revolutionizing business cards
Say goodbye to cluttered paper business cards. With a QR code, you can instantly share all your contact details, including your website and your online portfolio. You can forget about writing down contact info, forgotten cards, or misspellings. It’s far more efficient and memorable.
Video QR codes
Video QR codes are a powerful way to engage. These QRs link directly to product demos, tutorials, ads, or any video content you want to share. Whether you’re showcasing a new gadget or telling your brand’s story, it’s a scan-and-watch experience.
Restaurant QR code menus
Few changes have been as widespread as the shift to QR code menus. Sparked by the pandemic and now a permanent fixture in many restaurants, these menus offer a safe, contactless way to view dishes, place orders, and even pay. And since they’re digital, updates or daily specials can be made instantly—no reprinting required.

Marketing and advertising campaigns
QR codes have given a digital edge to traditional marketing. What used to be a static billboard, poster, or flyer is now an interactive touchpoint. One scan of the bar code, and a potential customer is instantly directed to a special offer, a promo video, or even an immersive AR experience. It’s marketing that moves—literally.
Product packaging
Today’s packaging does more than protect the product—it tells a story. By placing a QR code on product packaging, brands can invite customers to explore more. Scan the code to access how-to tutorials and traceability information. QR codes on packaging can also allow visitors to register for a warranty or sign up for a loyalty program.
Events and check-ins
From concerts to conferences, QR codes have streamlined the way we check in. Instead of printing tickets or waiting in line to sign forms, attendees can scan a QR code and walk right in. It’s faster, more efficient, and much easier to manage.
The real beauty of QR codes is in their balance: they’re incredibly simple to use, yet endlessly powerful in application. Whether you’re launching a campaign, packaging a product, or managing an event, QR codes store information in a way that’s instant, accessible, and built for today’s fast-moving world.
QR codes in marketing
QR codes have become indispensable in modern marketing and advertising campaigns—and it’s easy to see why. They serve as instant bridges between offline touchpoints and the digital world, making the user journey faster, smoother, and far more interactive.
With just a scan, a QR code can redirect someone from a flyer, business card, or billboard straight to a website—eliminating the need to manually type a URL.
For brick-and-mortar businesses, QR codes often link directly to Google Maps, helping customers find a store, event venue, or pop-up with just one tap. No confusion, no missed opportunities.
Print ads? They’re getting a digital upgrade. Adding QR codes to magazines, brochures, or posters transforms passive reading into active engagement—sending users to promotional videos, limited-time offers, or interactive product demos.
On social media, QR codes help users instantly follow brand profiles or jump into specific campaigns. Some even encourage real-time interaction by directing happy customers to leave a Google Review.
In short, when marketers embed QR codes into their campaigns, they’re not just adding a tech gimmick—they’re creating a seamless experience that connects the physical and digital worlds in a way today’s consumers expect.

Safety and QR codes
Most QR codes out there are safe, simple, and designed to make life easier. But like any digital tool, they can be misused.
Just as you’d be cautious clicking on a suspicious link or opening an unknown email attachment, it’s smart to treat QR code scans with the same care. Some malicious QR codes might redirect you to a malicious URL or attempt to gather personal information without your consent.
That doesn’t mean QR codes are dangerous by nature—they’re not. But they do require a bit of digital street smarts.
Always check the source before scanning. Is the QR code from a trusted brand, a verified business, or a reputable publication? If you’re unsure, it’s better to skip it.
You can also boost your safety by using a QR code scanner that offers security features, like URL previews or content warnings. These tools give you a heads-up about where the code leads before you commit to clicking through.
In the end, QR codes are safe when used wisely—so go ahead and scan, just stay alert.

Design and QR codes
Gone are the days when all QR codes looked the same. What once was just a black-and-white grid is now a customizable design element.
Brands can now personalize their QR code designs with unique colors, shapes, and even embedded logos—without losing functionality. It’s a way to maintain brand consistency while still using the powerful mechanics of QR code technology.
But design should never compromise function. A QR that looks amazing but can’t be scanned? That’s a fail.
When creating QR codes, it’s important to test readability across devices. Keep enough contrast, don’t crowd the edges, and make sure those all-important position markers are clearly visible. After all, the most stylish QR code still needs to do its job: get scanned.

QR codes on business cards
The humble business card has officially gone digital—and QR codes are leading the charge.
Instead of cramming every detail onto a small piece of cardstock, professionals now use a sleek QR code to connect beyond the paper. One quick scan can take a new contact to your website, portfolio, LinkedIn profile, or even a custom landing page—no typing, no hassle.
It’s more than just a space-saver. QR codes on business cards create an interactive experience that feels modern and efficient. You’re not just handing over contact info—you’re offering a direct link to your professional world.
It also keeps your design clean and minimal, letting the QR code do the heavy lifting while still making a strong impression.
In a world where first impressions often happen in seconds, a well-placed QR code adds both style and substance to your networking game.

Concluding thoughts on how QR codes work
Knowing how QR codes work it’s about understanding one of the most flexible tools in our digital toolbox.
With their unique structure and ability to store information compactly, QR codes have become a quiet powerhouse across industries. They’ve reshaped marketing and advertising campaigns, streamlined personal connections, modernized business cards, and made everything from ordering lunch to sharing a portfolio quicker and smarter.
And this is only the first step.
From dynamic QR codes that adapt to changing needs to design-forward QRs that reflect a brand’s personality, the possibilities are growing by the day.
So, the next time you scan a QR code, you’re tapping into a brilliant fusion of simplicity and sophistication. A small square that quietly powers some of today’s most seamless digital experiences.



